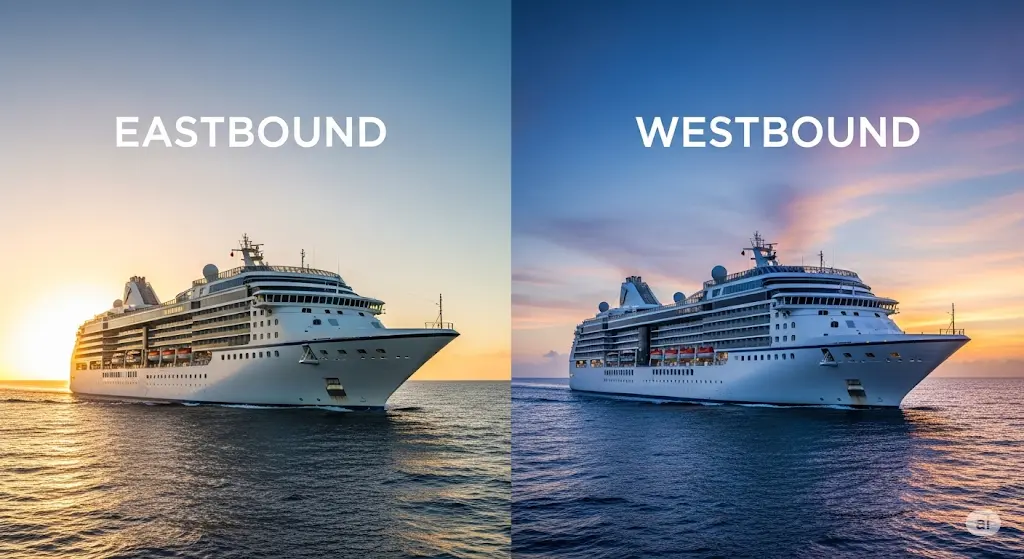
Eastbound vs. Westbound Transatlantic: Pros & Cons
Eastbound vs. Westbound Transatlantic: Pros & Cons 🚢✈️
Planning a transatlantic journey? Whether you’re dreaming of a leisurely cruise or a swift flight, the direction you choose – eastbound or westbound – can significantly impact your experience. From battling jet lag to maximizing daylight hours, understanding the pros and cons of each direction is crucial for a smooth and enjoyable trip. Let’s explore the key differences to help you decide which way is best for you.
The Crucial Difference: Time Zones & Jet Lag ⏰😴
The Earth’s rotation is the primary factor influencing the differences between eastbound and westbound travel. This rotation affects our perception of time and, consequently, our bodies.
- Eastbound Travel: Traveling east means chasing the sun. You’ll experience shorter days, and your body clock will need to adjust to an earlier time zone each day. This typically results in more severe jet lag, making you feel tired and disoriented.
- Westbound Travel: Traveling west means traveling against the sun. You’ll experience longer days, and your body clock will adjust to a later time zone each day. This generally results in less severe jet lag, as your body finds it easier to adapt to “gaining” time.
Eastbound Transatlantic: Pros & Cons ➡️
Pros:
- Arriving Earlier in the Day: If you’re flying, you’ll often arrive at your destination in Europe or Africa in the morning or early afternoon, giving you more time to settle in and start exploring.
- Potentially Cheaper Flights: Depending on the season and specific routes, eastbound flights can sometimes be slightly cheaper than westbound flights.
Cons:
- More Severe Jet Lag: As mentioned, traveling east is harder on your body clock, leading to greater fatigue and potential disruption of your sleep schedule.
- Shorter Days: You’ll experience fewer daylight hours during your journey.
Westbound Transatlantic: Pros & Cons ⬅️
Pros:
- Less Severe Jet Lag: Your body adapts more easily to “gaining” time, making westbound travel less tiring.
- Longer Days: You’ll enjoy more daylight hours during your journey.
Cons:
- Arriving Later in the Day: You’ll often arrive at your destination in the Americas in the evening or at night, potentially limiting your first-day activities.
- Potentially More Expensive Flights: Again, depending on the route and season, westbound flights can sometimes be pricier.
Beyond Jet Lag: Other Factors to Consider 🧭
While jet lag is a primary concern, other factors can influence your choice:
- Cruise Itineraries: Transatlantic cruises often have specific itineraries that may favor one direction over the other. Consider the ports of call and the overall length of the voyage.
- Flight Schedules: Check flight times and layovers. A shorter layover can be more appealing even if the direction isn’t ideal for jet lag.
- Personal Preferences: Some people are more sensitive to jet lag than others. Consider your own body clock and past travel experiences.
- Purpose of Travel: If you’re traveling for business and need to be sharp upon arrival, minimizing jet lag (westbound) might be crucial. If you’re on vacation and have more flexibility, the arrival time might be more important (eastbound).
Tips for Minimizing Jet Lag, Regardless of Direction 💡
While the direction of travel impacts jet lag, you can take steps to mitigate its effects:
- Adjust Your Sleep Schedule Gradually: Start shifting your sleep and wake times a few days before your trip.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after your journey.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: These can disrupt your sleep patterns.
- Eat Light Meals: Heavy meals can make you feel sluggish.
- Get Sunlight: Expose yourself to sunlight at your destination to help regulate your body clock.
- Consider Melatonin: This supplement can help regulate sleep cycles, but consult your doctor first.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Transatlantic Travel Direction ❓
Q: Is it always worse to travel eastbound?
A: While generally eastbound travel leads to more severe jet lag, the degree varies from person to person. Some people adjust quickly, while others struggle regardless of direction.
Q: Do transatlantic cruises have the same jet lag issues as flights?
A: Transatlantic cruises involve a slower transition between time zones, often with a full day between adjustments. This allows your body more time to adapt, resulting in less severe jet lag compared to flights.
Q: Are there specific flight routes that minimize jet lag?
A: Some experts suggest that flying north or south, rather than directly east or west, can lessen jet lag, but this is debatable and often impractical for transatlantic routes.
Q: How long does it typically take to recover from transatlantic jet lag?
A: Recovery time varies, but a general rule is one day per time zone crossed. For a typical transatlantic flight, this could mean 5-7 days to fully adjust.
Q: Is there any scientific evidence to support the difference between eastbound and westbound jet lag?
A: Yes, numerous studies have shown that our circadian rhythm (internal body clock) is more easily disrupted when we travel east, supporting the common experience of more severe jet lag.
Conclusion: Choose Your Direction Wisely! 🌟
The decision between eastbound and westbound transatlantic travel depends on your priorities. If minimizing jet lag is paramount, westbound is generally preferred. If arriving early is more important, or you find a significantly better flight deal, eastbound might be the better choice. By weighing the pros and cons and taking steps to manage jet lag, you can ensure a smoother and more enjoyable transatlantic journey, regardless of direction. Bon voyage!
📂 Explore More in These Categories
Best Cruise Destinations in 2025: Caribbean, Europe & Bucket List Ports
Compare Cruise Lines – MSC vs Royal, Carnival vs Norwegian & More